Discovering the Fermentation Edge: The Resurgence of Fruit Vinegars in Gourmet Foods
Fruit vinegars are a versatile artisanal ingredient celebrated for their distinct flavors, health b…….

Fruit vinegars are a versatile artisanal ingredient celebrated for their distinct flavors, health benefits, and culinary applications. Crafted through the fermentation process of various fruits such as apples, berries, grapes, and tropical fruits, these vinegars offer a range of taste profiles from sweet to tart. They are not only prized for their ability to enhance the flavor of dishes like salads, dressings, fermented vegetables, and baked goods but also for their nutritional contributions, including prebiotic fiber (the 'mother') and antioxidants like anthocyanins, flavonoids, and resveratrol. The demand for these natural, health-promoting vinegars is on the rise, with consumers increasingly opting for organic, small-scale productions that align with sustainable and clean labeling practices. As the culinary world becomes more adventurous and health-conscious, fruit vinegars are set to play a significant role in elevating the taste and nutritional value of meals across various cuisines.
Exploring the role of fruit vinegars within the fermented foods market unveils a rich tapestry of flavors, history, and health benefits. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of fruit vinegars, from their ancient origins to their emergence as a key ingredient in contemporary artisanal products. We’ll traverse the diverse landscape of fruit vinegars, including apple cider and exotic berry variations, and reveal the meticulous craft behind their production. Nutritional insights highlight their health-promoting properties, while innovative applications showcase their potential to elevate fermented foods. As we peer into the future, a growing trend towards unique and organic fruit vinegars suggests an exciting evolution in this market sector. Join us as we ferret out the intricacies of fruit vinegars’ impact on the culinary world.
- Exploring the Versatility of Fruit Vinegars in Fermented Foods
- The Historical Roots and Cultural Significance of Fruit Vinegars
- Types of Fruit Vinegars: From Apple Cider to Exotic Berry Variants
- Crafting Fruit Vinegars: The Fermentation Process and Its Nuances
- Nutritional Benefits and Health Implications of Incorporating Fruit Vinegars in Diets
- Innovative Applications of Fruit Vinegars in Artisanal Fermented Products
- Future Trends: The Growing Demand for Unique and Organic Fruit Vinegars in the Market
Exploring the Versatility of Fruit Vinegars in Fermented Foods

Fruit vinegars have long been a staple in culinary traditions around the world, offering a unique blend of tartness and depth that can elevate the flavor profile of various dishes. In the realm of fermented foods, these versatile condiments play a crucial role, not only adding a distinct taste but also contributing to the fermentation process itself. The natural acetic acid present in fruit vinegars acts as a natural preservative while imparting a complex flavor that can complement the tangy and sour notes inherent in fermented foods. From apple cider vinegar to balsamic, each type of fruit vinegar brings its own nuanced character, which can be exploited to enhance the taste and texture of fermented items such as kimchi, sauerkraut, and kefir. The use of these vinegars during fermentation can influence the end product’s acidity levels, thereby affecting its shelf life and flavor maturation. Moreover, fruit vinegars are a sustainable choice, often produced through traditional methods that have minimal environmental impact. As consumers become more conscious of the ingredients in their food and seek out healthier and more natural options, fruit vinegars stand out as an ingredient of choice for those looking to explore the boundaries of fermentation and taste.
The Historical Roots and Cultural Significance of Fruit Vinegars

Fruit vinegars, with their historical roots stretching back to antiquity, have played a significant role in culinary traditions around the globe. From ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and Romans, who used apple cider vinegar for its health benefits, to modern-day gastronomy, fruit vinegars have been fermented for both their flavor-enhancing properties and their nutritional value. The process of fermentation, whereby the natural sugars in fruit are converted into alcohol and then into vinegar by beneficial bacteria, has been refined over centuries, leading to a diverse array of vinegars with distinct tastes and aromas. These have been integral to various cuisines, each imparting their unique culinary identity. For instance, the sharp tang of balsamic vinegar from Modena, Italy, adds depth to salads and dressings, while rice vinegar is a staple in East Asian cooking, lending its mild sweetness to marinades and sauces. The cultural significance of fruit vinegars is evident not only in their widespread use but also in the myriad of traditions and folklore surrounding their production and consumption. They are a testament to humanity’s enduring relationship with fermentation, a process that not only preserves food but also transforms it into something new and valuable.
The cultural significance of fruit vinegars extends beyond the kitchen, influencing health practices and regional economies. In traditional medicine systems like Ayurveda and natural remedies, fruit vinegars have been revered for their potential health benefits. From aiding digestion to being used as natural preservatives, these vinegars have been an indispensable part of sustenance and well-being. The craft of producing fruit vinegars has been passed down through generations in various cultures, ensuring that the knowledge and skill required to create these beverages are preserved. Today, the global market for fruit vinegars reflects a blend of tradition and innovation, with new flavors and methods emerging while respecting the time-honored practices that have given rise to this versatile ingredient. As consumers increasingly seek out natural and authentic flavors, fruit vinegars continue to carve their niche in the fermented foods market, offering a tangible link to the past while satisfying contemporary tastes.
Types of Fruit Vinegars: From Apple Cider to Exotic Berry Variants

Fruit vinegars have carved out a significant niche within the fermented foods and beverages market, offering a diverse range of flavors and health benefits that cater to a wide array of consumer preferences. Apple cider vinegar, a longstanding favorite for its robust taste and numerous culinary uses, is often lauded for its potential health properties, including aiding digestion and supporting weight management. Beyond the classic apple variety, the market now bursts with an array of fruit vinegars, each imparting its unique characteristics to dishes and drinks alike. These include berry variants that span from the familiar strawberry to the more exotic likes of goji and acai, which not only introduce a spectrum of vibrant colors but also a multitude of flavors that can elevate salads, marinades, and even desserts. The use of fruit vinegars in food preparation is not merely a trend but a testament to the growing consumer interest in natural, additive-free ingredients that offer both taste and nutritional value. As the market for fermented foods expands, so does the variety of fruit vinegars available, each offering unique health benefits and culinary possibilities, making them an indispensable component for both professional chefs and home cooks alike. The innovation in this sector is driven by consumer demand for natural products with distinct flavors, reflecting a broader movement towards clean-label, artisanal food items that align with the values of health-conscious consumers and culinary adventurers.
Crafting Fruit Vinegars: The Fermentation Process and Its Nuances

Crafting fruit vinegars is a meticulous process steeped in tradition and culinary innovation, occupying a distinct niche within the fermented foods market. The journey from fruity to tangy begins with the selection of fresh, high-quality fruits that serve as the foundation for these flavorful condiments. Each type of fruit brings its unique character and color palette to the vinegar, from the rich hues of berries to the vibrant yellows of apples or pears. The fermentation process involves immersing the chosen fruit in water, allowing natural bacteria to initiate the transformation. This bacterial activity converts the sugars in the fruit into alcohol, which is then further oxidized into vinegar by a specialized acetic acid bacteria.
The nuances of this age-old craft lie in the delicate balance between science and artistry. Factors such as the type of mother culture used, the fruit’s sugar content, the temperature of the environment, and the duration of fermentation all play pivotal roles in shaping the final product. Artisans employ a variety of techniques to influence the vinegar’s flavor profile, including the addition of specific spices or herbs during fermentation, or the choice to use either a traditional open fermentation method or a more controlled, sealed environment. The result is a diverse array of fruit vinegars that cater to a wide range of culinary applications, from salad dressings and marinades to unique syrups and pairings with fine cheeses or chocolates. These vinegars not only add a tangy zest to dishes but also contribute to the nutritional value by offering beneficial probiotics and enzymes. The fermentation process, therefore, is both an art and a science, transforming simple fruit into a sophisticated ingredient that adds depth and character to the global culinary landscape.
Nutritional Benefits and Health Implications of Incorporating Fruit Vinegars in Diets
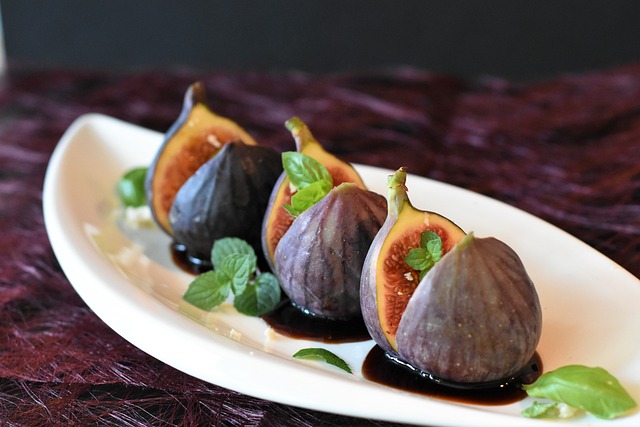

Fruit vinegars, derived from the fermentation of various fruits, offer a range of nutritional benefits that can enhance diets. These natural condiments are not just limited to culinary uses but also contribute to overall health and well-being. For instance, apple cider vinegar, a popular type of fruit vinegar, is rich in acetic acid, which has been studied for its potential impact on lowering blood sugar levels. This makes it particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those seeking to manage their blood sugar effectively. Moreover, the presence of ‘mother,’ a cobweb-like substance found in raw, unfiltered vinegars, contains enzymes and friendly bacteria that support gut health. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining digestive balance and can even aid in nutrient absorption.
Incorporating fruit vinegars into diets also provides a host of antioxidants, which are compounds that help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. The type of fruit used to make the vinegar dictates the specific antioxidants present; for example, berry vinegars may contain anthocyanins and flavonoids, while grape vinegars might offer resveratrol. These antioxidants are essential in preventing cellular damage that can lead to chronic diseases. Additionally, fruit vinegars can contribute to a lower risk of cardiovascular issues due to their potential effects on cholesterol and blood pressure levels. As part of a balanced diet, fruit vinegars can be a versatile tool for promoting health and longevity, offering a tangy addition to a variety of dishes while providing numerous health-promoting properties.
Innovative Applications of Fruit Vinegars in Artisanal Fermented Products

Fruit vinegars, a versatile and flavorful byproduct of the fermentation process, have carved out a niche in the realm of artisanal fermented products. These natural concentrates offer a robust and complex flavor profile that can elevate a variety of culinary creations. Innovative artisans are harnessing the potential of fruit vinegars to infuse new life into traditional fermented foods, such as pickles, sauerkraut, and kimchi. The unique acetic acid content in fruit vinegars not only imparts a tangy zest but also acts as a natural preservative, extending the shelf life of these products while enhancing their taste. For instance, apple cider vinegar, with its subtle sweetness, can add a fruity depth to fermented vegetables, while balsamic vinegar’s rich and complex flavor can transform a simple salad dressing into a gourmet experience. Additionally, the use of fruit vinegars in the production of sourdough bread has become a trend among bakers seeking to introduce distinct flavors and improve the fermentation process, resulting in loaves with an enhanced crust and more nuanced taste. These innovative applications showcase the versatility of fruit vinegars as key ingredients that can add a unique twist to artisanal fermented products, delighting consumers with new and exciting culinary experiences.
Future Trends: The Growing Demand for Unique and Organic Fruit Vinegars in the Market

The landscape of fermented foods is evolving, with a notable uptick in the demand for unique and organic fruit vinegars. Consumers are increasingly seeking out these products not just as flavor enhancers but also as natural ingredients that offer health benefits. The future trends indicate a significant shift towards more artisanal and authentic vinegar varieties, which often come from small-scale producers. These vinegars, crafted from an array of fruits such as berries, apples, pears, and tropical fruits, are gaining popularity for their diverse flavor profiles and the rich nutrients they contribute to culinary creations. The organic aspect is particularly appealing, as it aligns with a growing consumer preference for sustainable and environmentally friendly products. This trend is expected to persist and even accelerate as health-conscious consumers and food enthusiasts look for new ways to incorporate these versatile condiments into their diets and recipes.
The proliferation of organic fruit vinegars in the market is also a testament to the increasing interest in clean labeling and transparent supply chains. Manufacturers are responding by emphasizing the natural fermentation processes and the high-quality ingredients used in their products. The unique characteristics of each fruit variety result in a wide spectrum of flavors, from sweet to tart, which can be used to add complexity to dishes or as standalone beverages. As the demand for these niche vinegars continues to rise, innovation in flavor development and production techniques is likely to follow suit, further enriching the market with diverse offerings that cater to both traditional and modern tastes.