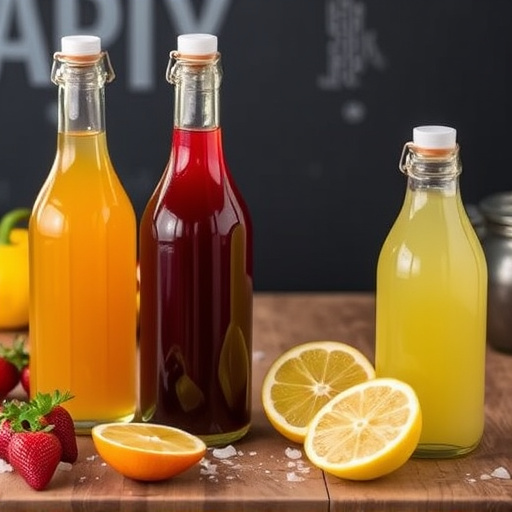
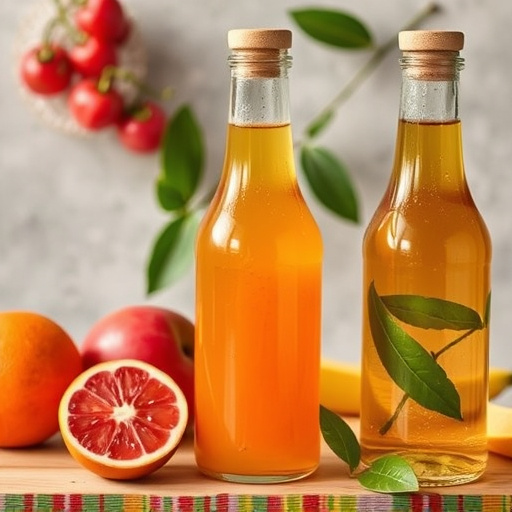
Balsamic vs Fruit Vinegar Showdown: A Guide to Their Flavors and Uses
Fruit vinegars are a versatile addition to any kitchen, offering a spectrum of flavors from tangy t…….

Fruit vinegars are a versatile addition to any kitchen, offering a spectrum of flavors from tangy to sweet that can elevate any dish. These natural condiments, made by fermenting various fruits like apple cider, berry, and more, provide a lighter alternative to traditional balsamic vinegar. They are perfect for adding a fresh note to salads, marinades, and desserts or for infusing cocktails with a fruity zest. Apple cider vinegar, for example, is known for its balance of sweetness and acidity, while berry vinegars contribute a delightful fruitiness. Fruit vinegars are not only culinary assets but also may offer health benefits when incorporated into wellness-focused diets. Their diverse flavor profiles, shaped by the type of fruit used and the fermentation process, make them a dynamic choice for both traditional and modern recipes, demonstrating their adaptability in the world of gastronomy. These ingredients are celebrated for their ability to transform simple dishes into gourmet experiences with their distinctive tastes and brightening capabilities.
—
Vinegar enthusiasts and culinary connoisseurs alike recognize the transformative role of vinegars in elevating dishes. Among the myriad types, balsamic vinegar and fruit vinegars stand out for their distinct flavors and versatile uses. This article delves into the nuanced world of these vinegars, offering insights into their origins, characteristics, and pairing potential. We will explore the rich tradition of balsamic vinegar, trace the diverse spectrum of fruit vinegars, compare their acidic and sweet notes, and guide you on how to harmonize them with a variety of ingredients and cuisines to create culinary masterpieces. Join us as we dissect the essence of balsamic vinegar and celebrate the vibrant flavors of fruit vinegars.
—
- Unraveling the Essence of Balsamic Vinegar: A Deep Dive into Its Origins and Usage
- Exploring the Spectrum of Fruit Vinegars: Flavor Profiles and Versatile Applications
- Comparing Acidity and Sweetness: The Differences in Taste Between Balsamic and Fruit Vinegars
- Pairing Perfection: How to Match Balsamic and Fruit Vinegars with Complementary Ingredients and Cuisines
Unraveling the Essence of Balsamic Vinegar: A Deep Dive into Its Origins and Usage

Balsamic vinegar, a storied condiment with a rich history rooted in Italy’s Emilia-Romagna region, has captivated culinary enthusiasts for centuries. Its creation involves a meticulous process of reducing grape must – the freshly pressed juice extracted from grape skins – into a concentrated syrup. This syrup is then aged in a series of wooden barrels, each imparting its unique flavor and character to the vinegar over time. The result is a complex, sweet-tart dressing that ranges from light to dark in color, with a depth of flavor that can elevate salads, meats, and desserts.
In contrast to traditional balsamic vinegar, fruit vinegars present a diverse array of options, each offering its distinct taste profile. These vinegars are crafted by fermenting various fruits, such as raspberry, peach, or fig, along with their complementary flavors and natural sugars. The fermentation process transforms the fruit’s natural sweetness into a tangy, aromatic vinegar, retaining the essence of the fruit while offering the acidity characteristic of vinegar. Fruit vinegars are incredibly versatile, finding their place in everything from marinades and vinaigrettes to cocktails and savory dishes, making them a popular alternative for those seeking a broader range of flavors beyond the classic balsamic. Whether used to brighten a dish or as a sweet complement to fruits and desserts, fruit vinegars are a testament to the versatility and innovation in the world of vinegar production.
Exploring the Spectrum of Fruit Vinegars: Flavor Profiles and Versatile Applications

Fruit vinegars present a delightful and diverse array of flavors that can elevate culinary creations. These natural condiments, derived from various fruits, offer a spectrum of tastes ranging from tart to sweet, with each type imparting its unique character. Apple cider vinegar, for instance, provides a balance of sweetness and acidity, making it a versatile choice for salad dressings, marinades, and even as a component in beverages. Berry vinegars, on the other hand, can introduce a fruity tang to desserts or combine with herbs for a refreshing vinaigrette. The flavor profile of each fruit vinegar is influenced by its source fruit and the fermentation process, resulting in nuanced variations that can complement a wide range of dishes. Their applications extend beyond the palate; they are also celebrated for their potential health benefits and are often incorporated into wellness routines. In the realm of gastronomy, fruit vinegars serve as an innovative ingredient to add brightness and depth to both sweet and savory preparations, showcasing their versatility in the culinary arts.
Comparing Acidity and Sweetness: The Differences in Taste Between Balsamic and Fruit Vinegars

Fruit vinegars encompass a diverse range of flavors and intensities, each reflecting the fruit from which they are derived. Unlike traditional balsamic vinegar, which boasts a complex profile that leans towards sweetness tempered by acidity, fruit vinegards offer a spectrum of tastes ranging from the fruit’s natural character to variations infused with additional flavors. The acidity in fruit vinegars can vary significantly; for example, apple cider vinegar is typically more tart compared to berry-based vinegars, which may carry a subtler, fruitier zing. This variability makes fruit vinegars versatile in culinary applications, where they can add both brightness and nuanced fruit notes to dishes.
In contrast, traditional balsamic vinegar, such as those from Modena or Reggio Emilia, Italy, is characterized by its syrupy consistency and a balance of sweet and sour elements. The grape must cooking process used in the production of balsamic vinegar concentrates the sugars, resulting in a product that is inherently sweeter than many fruit vinegars. The acidity in balsamic vinegar is complementary to its sweetness, creating a harmonious flavor profile that can stand up to robust flavors while also providing a counterpoint to the richness of certain foods. This balance makes balsamic an excellent choice for dressings, marinades, and as a finishing touch to enhance the flavors of a dish without overpowering them.
Pairing Perfection: How to Match Balsamic and Fruit Vinegars with Complementary Ingredients and Cuisines

When incorporating balsamic or fruit vinegars into culinary creations, pairing them with the right ingredients and cuisines elevates a dish from ordinary to extraordinary. Balsamic vinegar, with its deep, complex flavor profile that ranges from tart to sweet, often complements robust dishes. It pairs beautifully with fresh berries, ripe peaches, or figs, where it can accentuate the natural sugars of the fruit without overpowering them. The rich and syrupy balsamic reduction is particularly well-suited for pairing with grilled meats, roasted vegetables, and hearty salads. It lends a harmonious balance to the flavors, creating a symphony of taste that is hard to replicate.
On the other hand, fruit vinegars, which are made from a variety of fruits such as apples, pears, raspberries, or strawberries, offer a lighter and more varied taste spectrum. They are perfect for brightening up vinaigrettes, adding a refreshing zing to fish dishes, or infusing a light touch to desserts. The choice of fruit vinegar can be tailored to the specific dish, with each type imparting its unique flavor characteristics. For example, apple cider vinegar is versatile and can enhance the flavors of fall dishes, while raspberry vinegar brings a tart and berry-like essence to summer salads or sorbets. These vinegars are a testament to how the right ingredient can transform a dish, adding a level of complexity and depth that makes each culinary experience memorable. When experimenting with fruit vinegars, consider the other ingredients’ flavors and the desired outcome of the dish to ensure a harmonious and delightful pairing.